DDoS attacks sound very familiar as virtually any person has heard about them. They happen quite often, and webmasters try to go the extra mile to protect their servers from these attacks. However, it’s not that easy to stay safe.
Even though so many Internet users are aware of DDoS attacks, not all of them know what exactly these threats look like. Therefore, it’s even harder to come up with a security solution. In this article, we will talk about DDoS attacks in depth, pay attention to every type of this threat, and see how webmasters can protect their websites.
What is a DDoS attack?
DDoS stands for “Distributed Denial of Service”. It’s a non-intrusive cyber threat that aims to take down or at least slow down a target website by overwhelming its server with a lot of requests. To succeed, a malefactor has to create traffic that will be larger than the target server can handle or send forged requests.
Performing a DDoS attack, a malefactor tries to understand the limits of the server by creating random spikes of traffic. He tries to use vulnerable spots like search functions to complete the attack. A malefactor creates fake traffic with a botnet - a network that consists of a large number of compromised devices from computers and mobile phones to IoT gadgets. Thus, a DDoS attack doesn’t harm just a target server. It involves lots of generic users who might be not even aware of their devices being used for malicious purposes.
A DDoS attack is successful when it can slow down or put down a server so that users can’t access the website or application hosted on it. As a result, the site owner loses revenue and gains a headache trying to fix performance issues. Moreover, this threat increases the bounce rate of the website, thus lowering its positions in search engines.
The signs of a DDoS attack:
- The pages load very slowly
- The site doesn’t respond
- Users can’t access the site
- If the user is a target - they will have issues with their internet connection
DoS and DDoS attacks - are they the same?
They are very lookalike. But the difference is in their scope. A DoS attack comes from just one source, and a DDoS attack comes from a lot of sources. A DDoS attack on a very large scale can harm even thousands of systems at once.
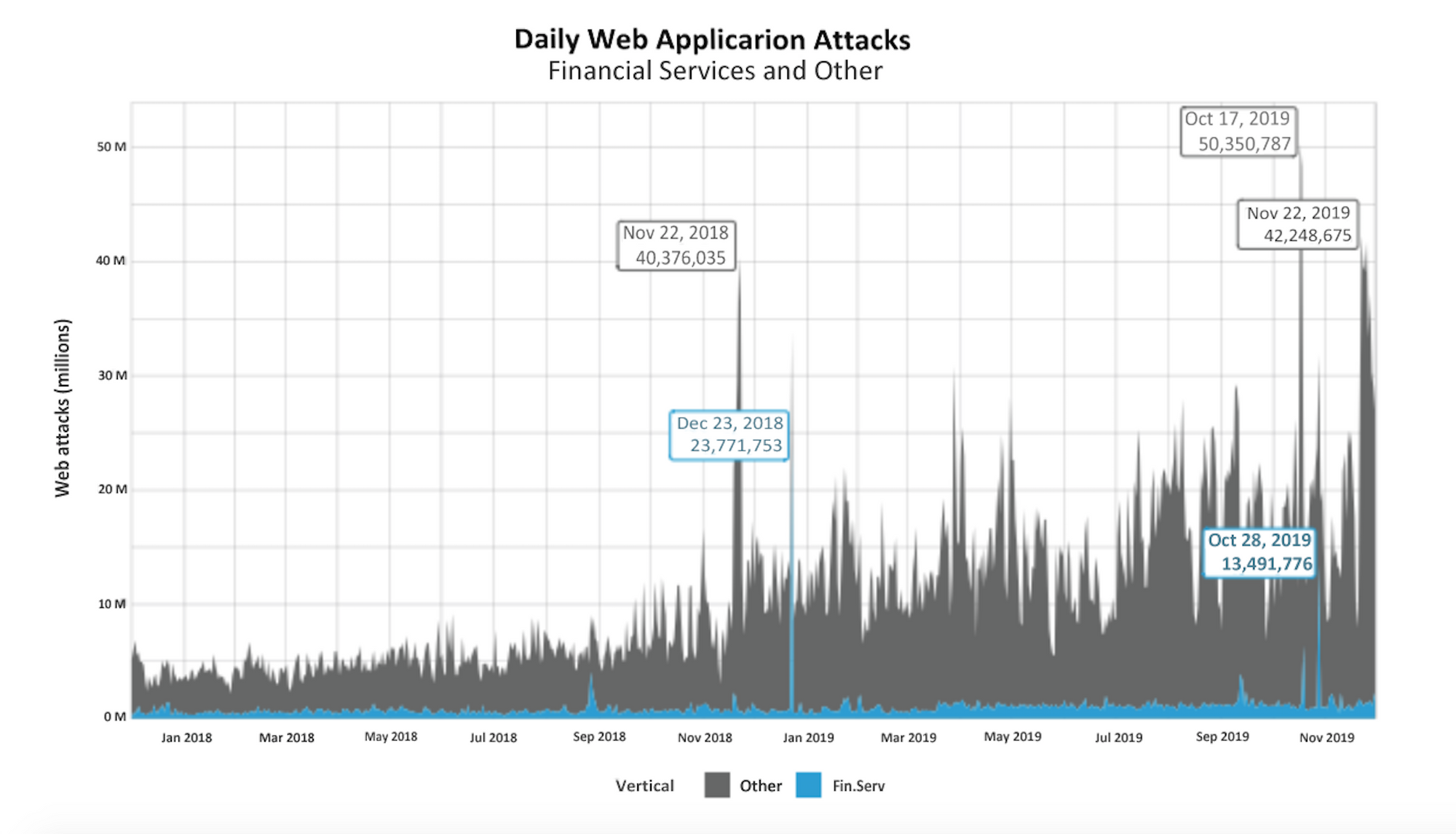
It’s extremely hard for most servers to deal with a DDoS attack since it often involves thousands of bots that send hundreds of requests every second. Also, there is such a thing as amplification. A malefactor can fool the server by making a host response to the request to a wrong destination. Then the server will process 1 byte of the incoming request and then, say, 100 bytes for the reply.
Why do malefactors perform DDoS attacks?
There are several reasons why would they threaten the target website.
To ask for a ransom
It sounds very barbaric, but this approach still exists today. An attacker sends an email to an owner of the target website telling about his intentions to perform a DDoS attack. In the email, he asks for a ransom. And to prove that he is serious, a malefactor follows this message with a short small attack.
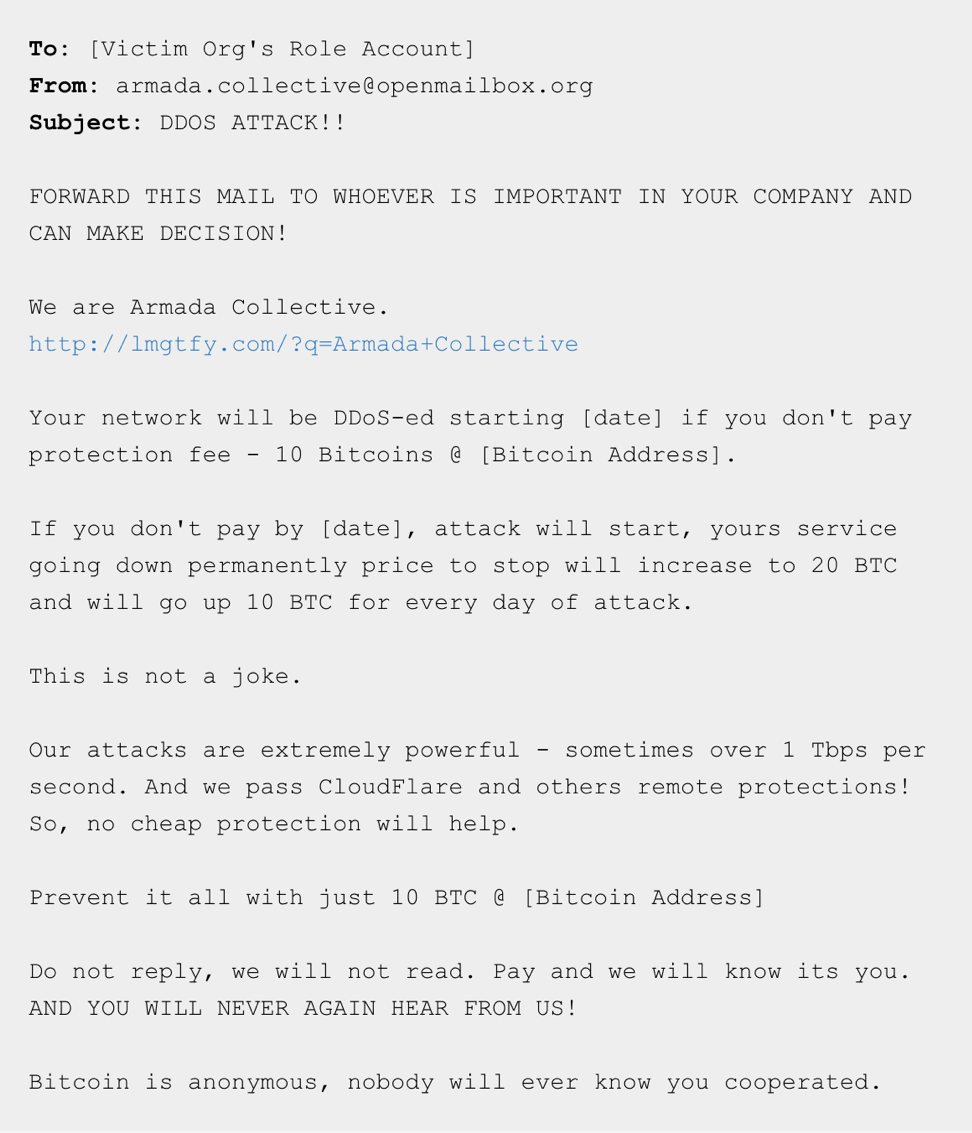
Quite often, such threats are just a fake performance, and a person who sends this email won’t really perform an attack. However, website owners tend to get scared and pay a ransom. That’s why it’s important to have solid protection from cyber threats - to be able to just ignore such threats. If you still don’t have such a safeguard, King Servers will gladly provide you with the protection from DDoS attacks.
To send a message
Many DDoS attacks are targeted on some government or specific business sites. By shutting them down a malefactor tries to make a statement. Usually, this approach is used to protest corporate, financial, political, or some other agenda. Also, hackers can perform attacks to just flex their skills in front of their community.
To damage a specific target
Malefactors will gladly perform a DDoS attack if they get paid. Then their goals are quite clear. In this case, we need to look into the intentions of the one who pays hackers for this attack. Often, this is how companies try to deal with their competitors. They will hire a hacker to take down the server of the rival hoping for the latter to lose positions and revenue.
Just for fun
We shouldn’t overlook the fact that hackers can perform attacks simply because they’re bored. A DDoS attack is a really fascinating challenge as a malefactor has to create the traffic and deal with the security measures the target server has. So it’s very appealing, especially for a young hacker, to take down some big website.
Kinds of DDoS attacks
Hackers have quite many approaches to performing this cyber threat. We will cover the most popular ones so that you can understand more in-depth how DDoS attack works.
Based on the volume of traffic
This kind of a DDoS attack depends on the volume of traffic a hacker manages to create. The goal of such a threat is to overwhelm the bandwidth of a target server or to overuse its CPU or IOPS. For this tactic, a malefactor needs to have more resources than the target server does. Considering that most website owners use shared or VPS hostings, this approach for a DDoS attack is often successful if no protection is implemented.
There are three kinds of volume-based DDoS attacks. The UDP flood type involves a hacker sending numerous User Datagram Protocol packets to random ports of the server. These packets make the server look for applications that would match the datagrams. But the host is unable to find them because they don’t exist. So it sends an error message back to the source of the request. Such UDP packets overwhelm the server by overusing its resources and make it go down.
Another approach is to send numerous spoofed ICMP requests from different IP addresses. This quickly drains all the resources of a server making it reboot or just significantly slowing down its performance. And finally, hackers can send ping packets from different IPs. It works quite like the tactic with ICMP packets, but the difference is that it’s very hard to detect ping packets and spot the attack.
Based on the protocol
Protocols are the cornerstone of the Internet. To perform a DDoS attack malefactors use vulnerabilities of the Layer 3 (Transport Control Protocol), and Layer 4 (email and file transfer protocols). Then the tactic is to overwhelm the server by sending more packets to these protocols than the network can bear.
There are two approaches to protocol-based DDoS attacks. The first one is to send pings targeted at apps or hardware of a destination server. It’s a very dangerous threat since one hacker can take down the whole data center using this tactic.
Another way is to use vulnerabilities of Layer 3. This protocol uses a three-way handshake that involves the client, the host, and the server. Malefactors send packets to the targeted server to the point when they drain all the resources of the table memory connection.
Applications as a target
Every server has some apps running on it so that the webmaster can control the site. Attackers target web servers and even control panels and content management systems. Their aim is to interrupt the work of the app and, consequently, of the whole website.
Such attacks have a smaller scale, and they tend to remain unnoticed until the damage is done. This tactic requires fewer resources for a hacker to attack the site and overwhelm the CPU or the memory of the server. One of the approaches malefactors use is to attack the DNS server of the website. They use the botnet to create traffic of TCP/UDP/ICMP floods and make the service unavailable for other users because the DNS server is overloaded.
Another way hackers use is to target the URLs that allow them to bypass caching. Thus, malefactors exhaust all the servers without being cached. This kind of attack is very hard to detect as it appears like the behavior of a generic user. Finally, there are HTTP flood attacks that are virtually impossible to detect. Using this approach, hackers overload only a certain part of a target server, and their activity looks very natural. Such an attack doesn’t even require a lot of resources from a malefactor. If executed correctly, even just a few requests per second can overwhelm the app and backend databases, and drain all the resources of the server.
How to protect your server from DDoS attacks?
To stay safe you need to perform a set of actions and monitor your network constantly. This is a complex process. That’s why webmasters usually trust the protection to security specialists.
But if you’re willing to figure the protection yourself, here is what you can do:
- Enable WAF - WAF stands for the Website Application Firewall. It helps to protect the website from malicious traffic by understanding the type of data that’s allowed for protocols.
- Block specific countries - most DDoS attacks come from China, Russia, and Turkey. You can try not users from these locations to visit your website.
- Monitor the traffic - be aware of traffic peaks and take action if you detect suspicious activity.
- Keep an eye on logs - they can tell you a lot about what’s going on with a server so that you can detect slow application-layer attacks.
These actions are quite cumbersome to execute if you’re not a security specialist. That’s why we at King Servers offer extended DDoS protection that will keep malefactors away from your website. Our professionals can defend your server from all the types of DDoS attacks and keep it safe on all levels from hardware to applications.
We offer flexible pricing so that you can find a solution that’s suitable for your needs without paying too much. Our security team is working 24/7 to monitor your network and keep it safeguarded. And if you need additional help - the team is ready to step in at any moment.
It will take only 10 minutes to set up the anti-DDoS protection on your server. And then you can have greater peace of mind knowing that your website is safe. We also offer protected hostings that are already safeguarded from attacks. Just drop us a line if you want to stay safe from hackers.