By 2021, about 16 billion devices from the category of "Internet of things" will be functioning worldwide. But progress has not made life easier in some aspects. Botnets are a vivid example of using good technologies for bad intentions. A relatively new type of cyber attack where IoT devices are used is becoming more and more relevant every day. So, how do DDOS attacks occur through botnets and how can they be prevented? We will talk about this in this article.
What is a botnet?
A garbage can with filling sensors, a security video surveillance system with the function of saving records, a smart set-top TV box - all these devices connect IoT technologies. All the devices are connected to the network, so the data transfer is performed without human involvement.
A botnet is a chain of a large number of devices connected to the Internet. So, hackers infect each device with malware, which makes it possible to keep complete control over them.
Cybercriminals use botnets for target attacks on Internet sites. Using a botnet, cybercriminals can steal people's data or gain unauthorized access. The most common way to use botnets is DDoS attacks.
Cyber attacks: how they can be launched through botnets?
The launch scheme is similar to the usual DDoS attack. However, hackers infect not users' computers, but their IoT devices. A majority of the modern devices have at least some vulnerabilities, for example, when owners do not change the default password. Cybercriminals simply connect to badly protected devices and create a botnet. Thus, botnet owners gain access to several thousand devices simultaneously, which makes it possible for them to conduct cyber attacks.
The most well-known attacks performed through botnets
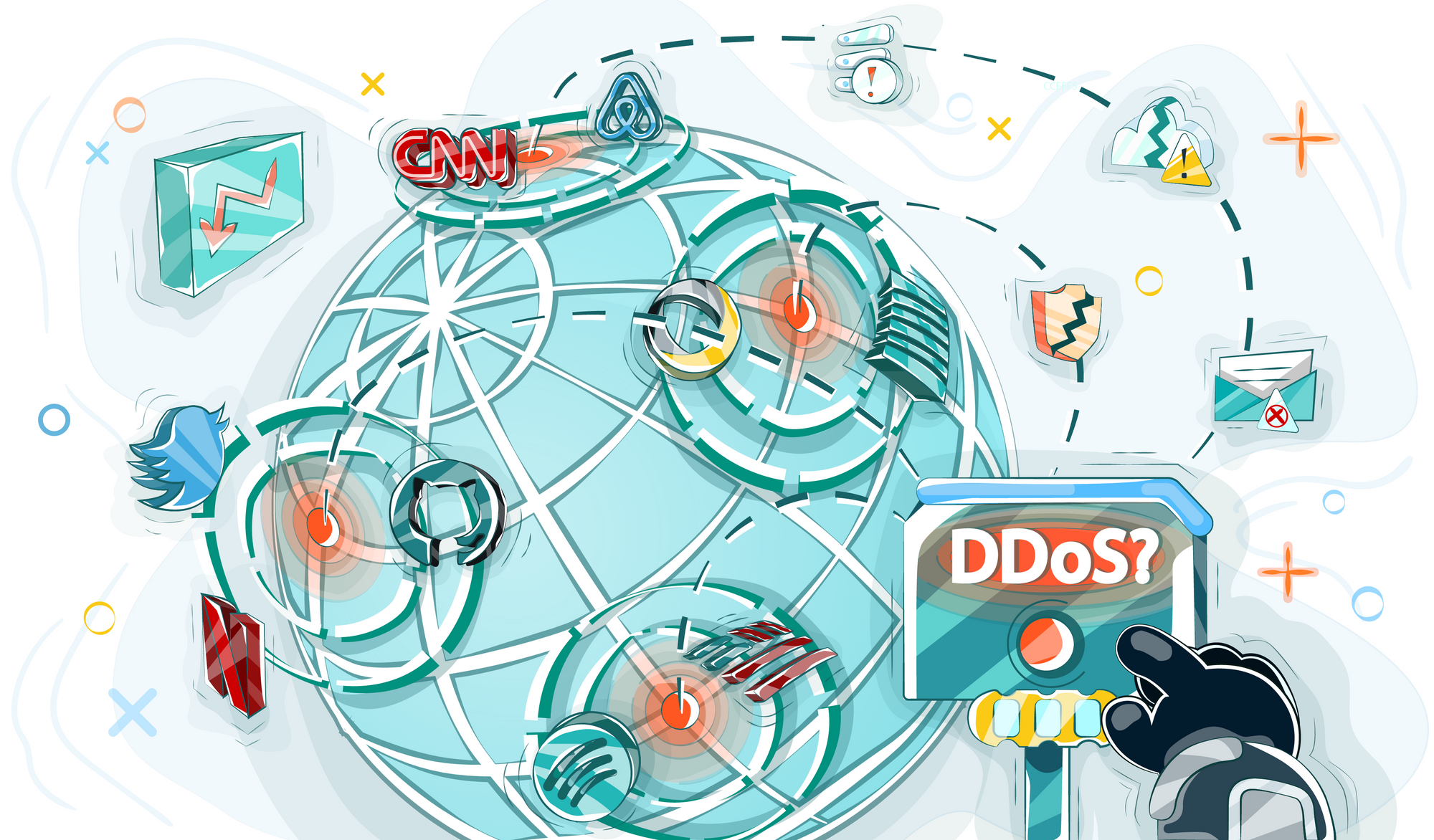
Many cyber attacks have gone down in history, and there are several interventions through botnets among them. The first largest botnet was Mirai. It was discovered by cybersecurity experts in September 2016. The initial reason for the gadgets infection was the default passwords set by manufacturers on their released devices. Brian Krebs' website was the first victim of the attack. Brian Krebs is a journalist who had previously written about bot networks. Then the American Dyn DNS operator was chosen by attackers as the next target. The largest world sites ceased to work because of this intervention (you can read more about this in this article). Also, with the help of Mirai, hackers attacked the European host OVH. According to estimates of further infections of devices, the original botnet infected approximately half a million of IoT devices.
Another raucous botnet was Reaper, also known as IoTroop. It was first used for attacks in the fall, 2017. Devices were hacked super fast, even faster than it was with Mirai. Not only poorly protected devices with default passwords were infected, but also devices from well-known manufacturers (such as D-Link). Subsequently, the botnet was used by attackers who directed an attack on large European banks.
How many devices are needed for a DDoS attack?
Tens of thousands of devices must be connected to perform a successful cyber attack. The specific number of bots will vary, depending on the cybercrime's ability to infect unprotected devices.
Interesting statistics are given by Akamai. So, in 2016, several customers of the company suffered from a cyber attack from 13 thousands of devices. It was enough to send almost 270 thousand requests per hour. In a DDoS attack in 2017, hackers attacked one of Akamai's customers through a network of more than 75 thousand bots.
Why is it difficult to prevent a botnets cyber-attack by yourself?
Botnet attacks are a hot topic for cybersecurity specialists. They are discussed actively in recent years, as the number of IoT devices is growing exponentially. Since the fight against botnets is difficult, preventive measures must be taken to be protected while manufacturers and authorized companies are trying to cope with the problem.
Vulnerable devices selling
Imagine an ordinary person who wants to buy a smart robot vacuum cleaner, which can be turned on while sitting in the office. Security is the last thing that will interest this man or woman (he/she may not even ask any questions about the security or ask one or two). Customers are interested in the gadget's functionality, its power, the status of the manufacturer, and, of course, the price. A person will likely choose a cheaper device, ignoring possible vulnerabilities.
IoT gadgets manufacturers do not always work on security. Any omission in the process of software development may lead to the creation of botnets and cyber attacks. Such products will always be in demand due to the low prices, so it's impossible to get rid of this problem yourself.
It's difficult or impossible to track the traffic
If an attack is a large one (as it was with previously described botnets Mirai or Reaper), the flow of requests is easy to notice and block. However, they are often used for smaller crimes, for example, for sending spam. In this case, Internet providers simply do not pay attention to him. This is also due to traffic tracking difficulties.
Infected devices are difficult to detect
It's worth mentioning that some organizations control the vulnerability of gadgets. Such companies as CrowdStrike report infected devices to providers from different countries. Those can contact the owners of the infected devices and report a problem. But, as it was previously mentioned, there are billions of IoT devices. And millions of them can be in the botnet chain. It's next to impossible to control the spreading of infected gadgets.
IoT devices are easy to infect
Most gadgets are an ideal target for installing malicious software. There are several main reasons for this:
- Round-the-clock operation of devices makes it possible for them to be compromised and used for an attack at any time, while there are no problems with limited bandwidth.
- There is no full control over the work of gadgets by an administrator.
- The slashed operating system based on Linux, which is often used to create IoT devices, makes it impossible to fully realize their security.
Besides, the owners themselves rarely notice that their device is infected with malware.
It's easy to create a botnet
Cybercriminals are often young people. Even in the case of the sensational Mirai botnet, the US government detained two students (not a group of dangerous criminals). This means that launching an attack through a botnet is easy, so long training and special knowledge are not required.
Try to google the way to create a botnet. On the very first page of the search engine, there will be a link to a detailed tutorial. No wonder, as botnets can be used not only in cyber attacks. However, their danger from this does not decrease.
The consequences of a botnet attack can be devastating. Sometimes device owners feel the result of an attack. The device may have reduced performance or some personal data may be stolen. The sites that fall victim to the DDoS attack often face even more serious consequences. We have already written about how cyber attacks can destroy your business. At best, the site simply will not function, but this will certainly lead to losses, especially if an internet-shop was attacked.
Effective protection against DDOS attacks
To avoid malicious interference and protect your site or server, you'd better think about cybersecurity in advance. Protection should be automatized, and King Server will help you with it.
We understand how dangerous DDoS attacks can be for your business, so we offer professional and effective protection of virtual and dedicated servers. Having ordered a service, you will get:
- Available resources at any time of the day;
- 10-minute tuning;
- 1 TB/s geographically distributed filtering.
Our customers can count on flexible prices. To make it possible for each customer to select the best option in terms of cost and needs, King Server offers different rates. So, you can determine the traffic and the number of protected domains yourself. We provide full 24-hour server protection from cyber-attacks. So, you won't have to be afraid of any botnets or cyber attacks!